Balancing of hydronic circuits
Modern conditioning units have to meet some fundamental criteria, namely ensuring a high thermal comfort and managing energy use. Choosing a heating system is becoming increasingly important. There are obviously economic reasons but also ecological reasons. The increasingly important EPB standard also plays an essential role. The influence and selection of a heating system and the right balance of an installation has a major impact on comfort and efficiency.
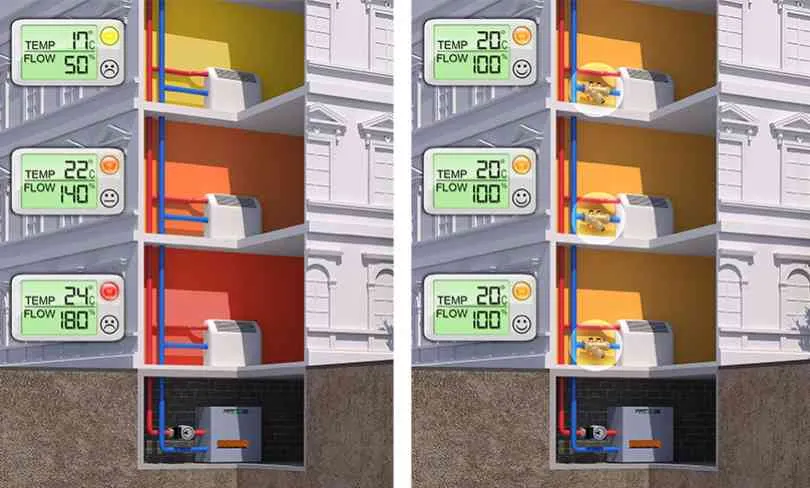
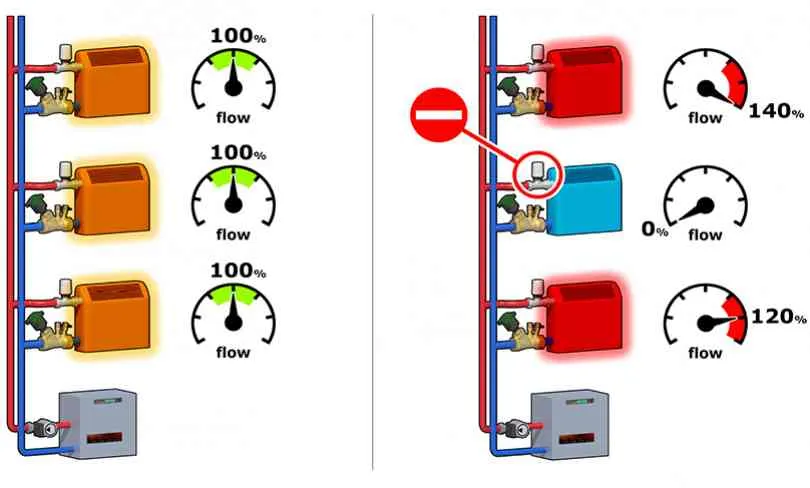
A properly balanced system is a system that provides the correct flow and power in all circumstances and areas.
The hydraulic imbalance causes non-uniform temperature zones between the various heat exchangers. This results in a reduced thermal comfort and increased energy consumption.
1. Energy loss through greater heat loss than were calculated.
2. Excessive water velocities in the pipes causing noise and possibly erosion.
3. Too high energy consumption and too low yields from the pumps because they are having to process too large a flow.
4. Too low a flow rate leads to the heating system producing too little capacity.
5. Heating of areas that should not be heated.
-
GUIDE "DEVICES FOR CIRCUIT BALANCING. 2015": brand-new, it introduces all products that balancing solutions that Caleffi can provide.
- TECHNICAL REPORT "DYNAMIC BALANCING OF HYDRONIC CIRCUITS": this report analyses the technical advantages of AUTOFLOW® automatic flow regulators used to dynamically balance hydronic circuits in air conditioning installations. Circuits are examined at full load and part load and balancing efficiency is compared to that obtained using traditional manual balancing valves.
- AUTOFLOW@ APPLICATION SHEETS: a set of application sheets describing various real installations that make good use of AUTOFLOW@ flow stabilisers. Each application sheet describes tthe functioning of the particular installation and provides a functional circuit diagram.
On our YouTube Channel several videos on balancing. Here we suggest the one on Pressure Independent Control Valve (PICV)