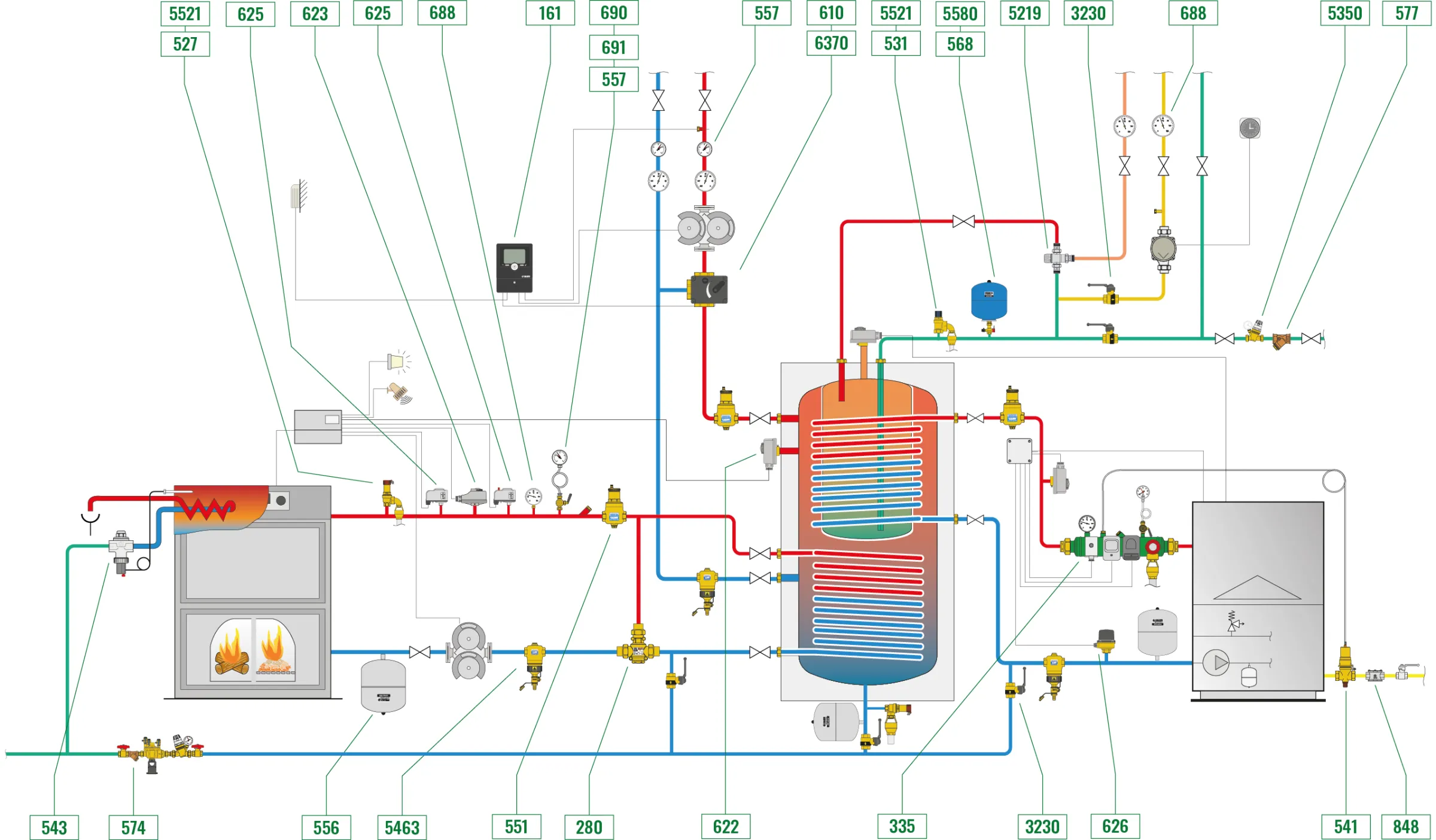
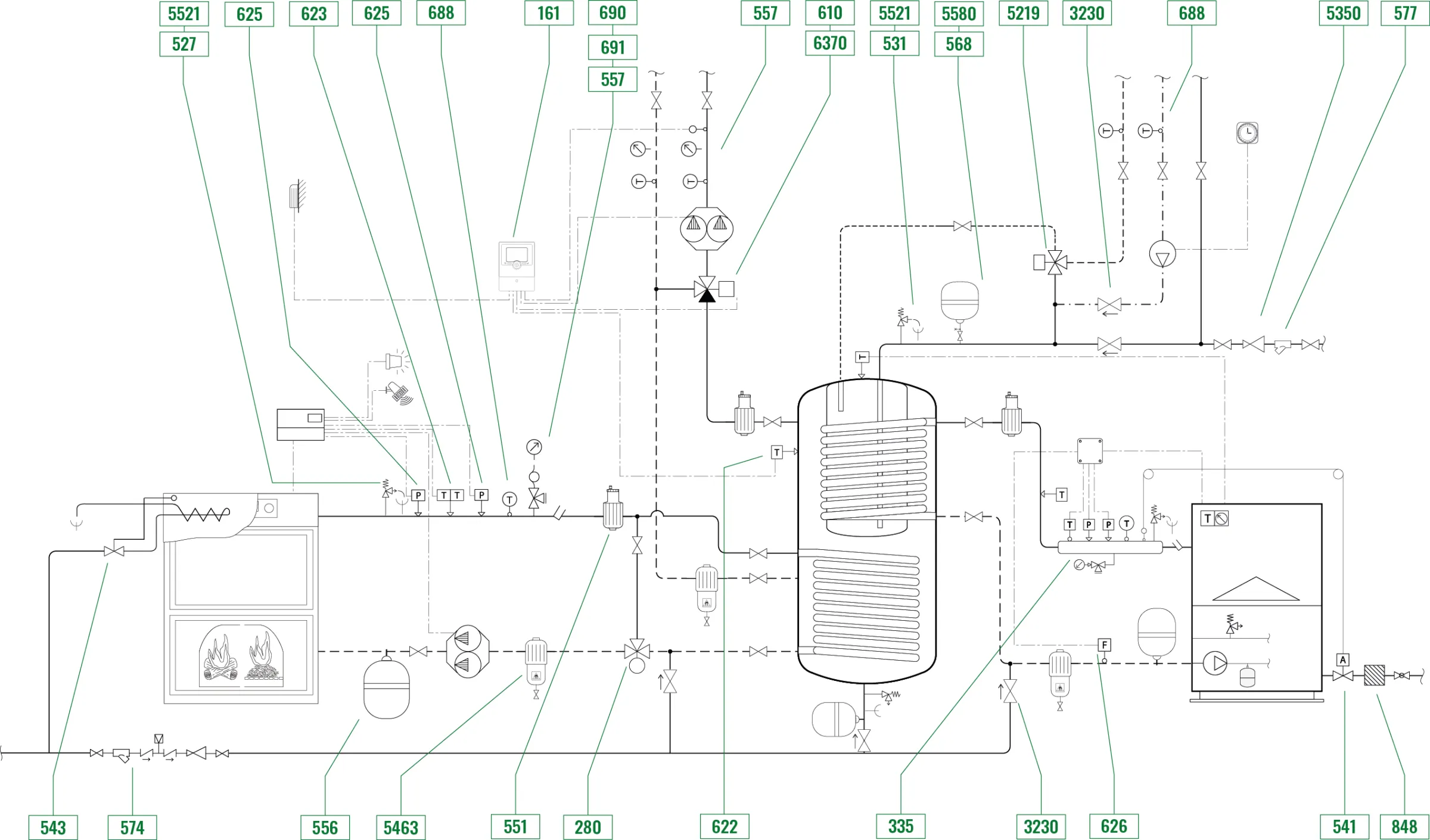
The central heating system can be divided into 4 zones:
Biomass boiler zone
This zone is essentially composed of:
· Boiler with automatic air supply
· High efficiency tandem circulation pump
· Mechanical three-way anti-condensation valve to prevent water with a temperature value that is too low from returning to the boiler
· Control, expansion and safety equipment
Traditional fuel-fired boiler zone
This zone is essentially composed of:
· Condensing boiler with internal circulation pump
· Control, expansion and safety equipment
Inertial tank zone with heating medium distribution
This zone is essentially composed of:
· “Tank-in-tank” combined water storage
· High efficiency tandem circulation pump
· Three-way regulating valve with climatic controller
Domestic hot water production and distribution zone
Domestic hot water is produced in the inner part of the inertial tank.
The tank-in-tank storage with dual heat exchanger makes managing the two heat sources easier. The thermostat on the storage tank or the room thermostat triggers the controller to manage the temperature of the biomass boiler. When it does not have a sufficient thermal load, it triggers the gas boiler. The DHW thermostat manages the boiler and inhibits heating if DHW production is required.
Note:
The control, expansion and safety equipment must be of appropriate size to reflect the heating capacity and specific characteristics of the system, in accordance with applicable laws and regulations.
If necessary, or if required by current legislation relating to water hardness, the heating system water must be suitably treated.


























