
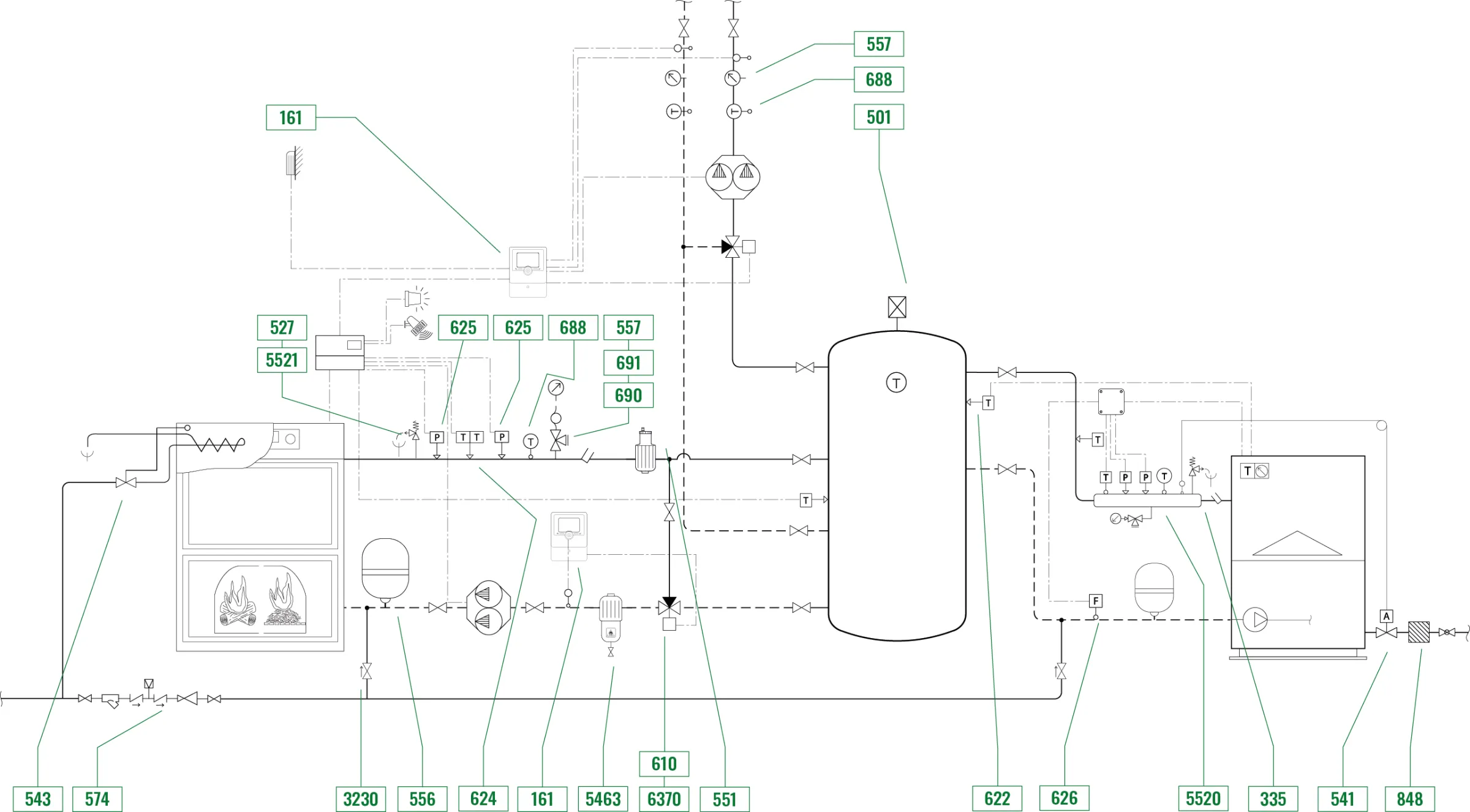
The central heating system can be divided into 3 zones:
Biomass boiler zone
This zone is essentially composed of:
- Boiler with automatic air supply
- High efficiency tandem circulation pump
- Three-way modulating valve with control unit to prevent water with a temperature value that is too low from returning to the boiler
- Control, expansion and safety equipment
- Charging unit with pressure reducing valve and backflow preventer
Traditional fuel-fired boiler zone
This zone is essentially composed of:
- Boiler with internal circulation pump
- Control, expansion and safety equipment
- Charging unit with pressure reducing valve
Inertial tank zone with heating medium distribution
This zone is essentially composed of:
- Inertial tank
- High efficiency tandem circulation pump
- Three-way valve with set point regulation
- Control and shut-off devices
- Dirt separator with magnet
This solution is generally used in systems with heat interface units, i.e. with zone outlets able to provide both heating and domestic hot water production.
The water temperature at the outlet to the radiators can be regulated to a value that generally falls between 60 and 65 °C;
The dirt separator with magnet intercepts and removes dirt particles normally suspended in the water of heating systems. In particular, the magnet is designed to intercept particles of magnetite, thus preventing them from collecting (and causing serious damage as a result) on the magnetic rotors of the new high-efficiency pumps.
If necessary, or if required by current legislation relating to water hardness, the heating system water must be suitably treated.
Note:
The control, expansion and safety equipment must be of appropriate size to reflect the heating capacity and specific characteristics of the system, in accordance with applicable laws and regulations.


















