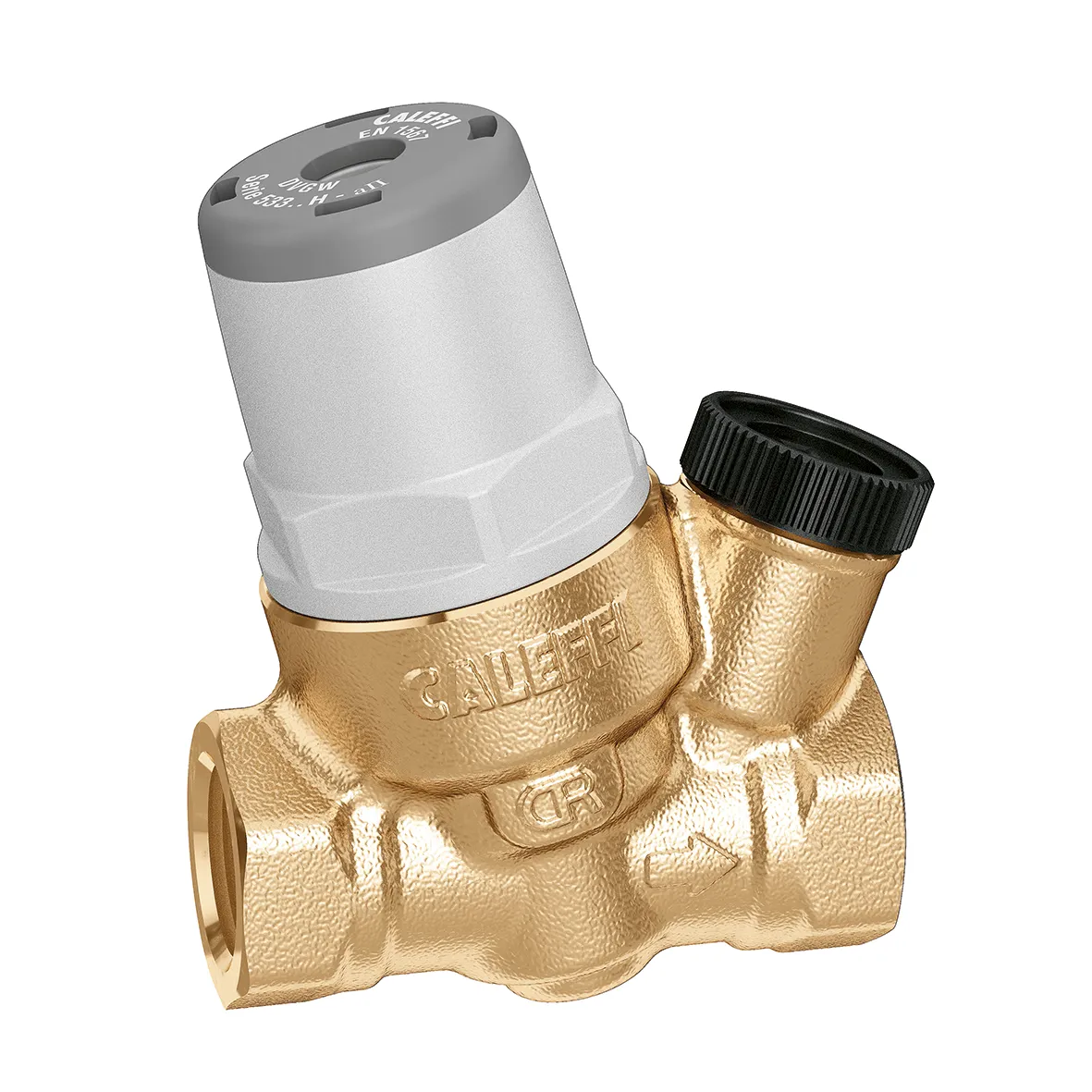
Inclined micro pressure reducing valve for special applications: for dispensing water, beverages and coffee machines.
Product Description
Inclined micro pressure reducing valve for special applications: for dispensing water, beverages and coffee machines.
Replaceable cartridge and strainer.
Certified to EN 1567.
PATENT PENDING
Technical data
Certifications






Download
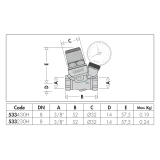
Drawings and specifications
| Part number | Note | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 533230H | With pressure gauge 0–10 bar | ||
|
2D drawings
3D models
Tender text
CALEFFI, 533230H.
Inclined micro pressure reducing valve for special applications: for dispensing water, beverages and coffee machines.
Replaceable cartridge and strainer. Certified to EN 1567.
Maximum upstream pressure: 16 bar. Medium temperature range: 2–80 °C. Adjustment pressure range: 0,8–4 bar. Maximum recommended flow rate: 6 l/min. Material: dezincification resistant brass DR "low lead".
SCIP code
957237bb-bf79-45bc-b0a7-38ee27802a52
|
|||
| 533430H | - | ||
|
2D drawings
3D models
Tender text
CALEFFI, 533430H.
Inclined micro pressure reducing valve for special applications: for dispensing water, beverages and coffee machines.
Replaceable cartridge and strainer. Certified to EN 1567.
Maximum upstream pressure: 16 bar. Medium temperature range: 2–80 °C. Adjustment pressure range: 0,8–4 bar. Maximum recommended flow rate: 6 l/min. Material: dezincification resistant brass DR "low lead".
SCIP code
957237bb-bf79-45bc-b0a7-38ee27802a52
|
|||
Faq - Frequent questions
Just remove the impurities. In the case of the 535 series pressure regulators (in the drawings), this procedure is extremely simple because the regulator insert is one element that can be unscrewed with a wrench. After cleaning, the insert must be installed. There is no need to recalibrate, the pressure will be maintained according to the setting on the knob. A similar procedure can be performed for the 533 series regulators, but these require the pressure to be re-set. The second case occurs in installations where the water pressure regulator is installed in the supply of the domestic hot water tank. Unfortunately, such installation is often performed when there is no expansion vessel in the cold utility water installation. Omission of such an important element results in periodic activation of the safety valve. This happens due to the increase in pressure in the tank during water heating.
The water pressure regulator stabilizes the pressure to the set value and it remains unchanged regardless of pressure fluctuations in the water supply network. The reducer, on the other hand, reduces the pressure by a certain amount, which means that when the pressure on the water supply side changes, the pressure at the outlet of the reducer will also change.
1. Contaminants have got into the sealing area of the regulator seat, which does not close properly and causes a slight leak, the pressure tends to equalize on both sides of the regulator. The situation occurs, of course, without flow, with closed draw-off points, i.e. when the regulator should be closed. 2. The pressure gauge shows the pressure of water heated in the domestic hot water tank when the regulator is installed upstream of the tank. The heated water, under the influence of thermal expansion, flows back towards the pressure regulator and the high pressure has no outlet.
In such a case, we are most likely dealing with the phenomenon of cavitation. This phenomenon occurs when we reduce the pressure from high to quite low, then the water flow speed increases rapidly between the regulator's plug and its seat, which causes the pressure to drop to the so-called evaporation pressure. Air microbubbles are then produced. When the pressure begins to increase slightly again, the bubbles rapidly implode, which in turn produces a shock wave, damaging the regulator walls, seat, seals and causing the above-mentioned noise.